队列
队列的含义
队列是一种先进先出(First In First Out, FIFO)的数据结构。类似我们排队的样子,站在队伍最前面的人拿到东西后离开,新来的人要站在队伍的最后。 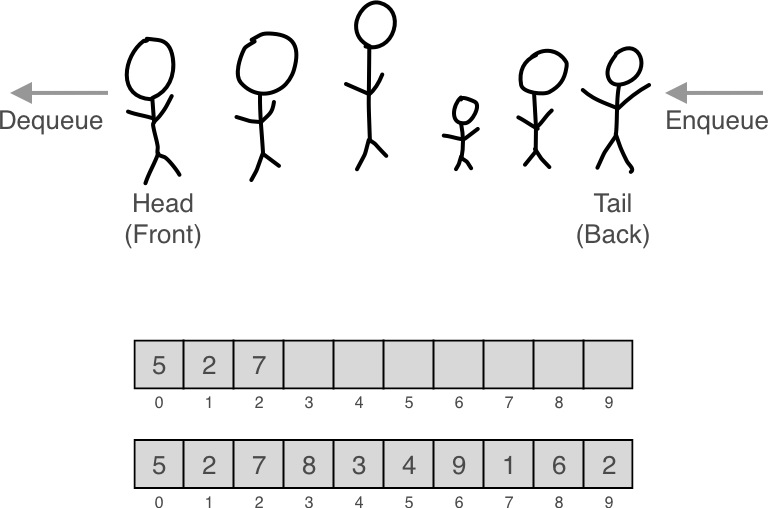
队列同样可以使用数组或者链表来实现。
数组实现队列
基于python用数组实现一个Queue类,包含如下方法:
enqueue- adds data to the back of the queuedequeue- removes data from the front of the queuefront- returns the element at the front of the queuesize- returns the number of elements present in the queueis_empty- returnsTrueif there are no elements in the queue, andFalseotherwise_handle_full_capacity- increases the capacity of the array, for cases in which the queue would otherwise overflow
Also, if the queue is empty, dequeue and front operations should return None.
1. 创建queue类和__init__方法
Define a class named
Queueand add the__init__methodInitialize the
arrattribute with an array containing 10 elements, like this:[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]Initialize the
next_indexattributeInitialize the
front_indexattributeInitialize the
queue_sizeattribute测试用例:1
2
3
4
5
6class Queue(object):
def __init__(self):
self.arr = [0 for i in range(10)]
self.next_index = 0
self.front_index = -1
self.queue_size = 0### 2. 增加1
2
3q = Queue()
print(q.arr)
print("Pass" if q.arr == [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] else "Fail")enqueue方法Take a value as input and assign this value to the next free slot in the array
Increment
queue_sizeIncrement
next_index。这里需要取模(modulo operator%),因为用数组实现队列时会出现出队后数组前面变空的现象,为了再利用数组前面出队后的空间,所以对数组空间进行取模。这样就实现了理论上的环形数组(首尾相连)。If the front index is
-1(because the queue was empty), it should set the front index to0
1 | class Queue: |
3. 增加size, is_empty和front方法
- Add a
sizemethod that returns the current size of the queue - Add an
is_emptymethod that returnsTrueif the queue is empty andFalseotherwise - Add a
frontmethod that returns the value for the front element (whatever item is located at thefront_indexposition). If the queue is empty, thefrontmethod should return None.
1 | class Queue: |
4. 增加dequeue方法
- If the queue is empty, reset the
front_indexandnext_indexand then simply returnNone. Otherwise... - Get the value from the front of the queue and store this in a local variable (to
returnlater) - Update the
queue_sizeattribute - Return the value that was dequeued ### 5. 增加扩容函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35class Queue:
def __init__(self, initial_size=10):
self.arr = [0 for _ in range(initial_size)]
self.next_index = 0
self.front_index = -1
self.queue_size = 0
def enqueue(self, value):
# enqueue new element
self.arr[self.next_index] = value
self.queue_size += 1
self.next_index = (self.next_index + 1) % len(self.arr)
if self.front_index == -1:
self.front_index = 0
# TODO: Add the dequeue method
def dequeue(self):
if self.queue_size == 0:
self.front_index = -1
self.next_index = 0
return None
tmp = self.arr[self.front_index]
self.front_index = (self.front_index+1) % len(self.arr)
self.queue_size -= 1
return tmp
def size(self):
return self.queue_size
def is_empty(self):
return self.queue_size == 0
def front(self):
if self.queue_size == 0:
return None
else:
return self.arr[self.front_index]
define the _handle_queue_capacity_full method:
- Define an
old_arrvariable and assign the the current (full) array so that we have a copy of it - Create a new (larger) array and assign it to
arr. - Iterate over the values in the old array and copy them to the new array.
Then, in the enqueue method: * Add a conditional to check if the queue is full; if it is, call _handle_queue_capacity_full 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64class Queue:
def __init__(self, initial_size=10):
self.arr = [0 for _ in range(initial_size)]
self.next_index = 0
self.front_index = -1
self.queue_size = 0
def enqueue(self, value):
# TODO: Check if the queue is full; if it is, call the _handle_queue_capacity_full method
if self.queue_size == len(self.arr):
self._handle_queue_capacity_full()
# enqueue new element
self.arr[self.next_index] = value
self.queue_size += 1
self.next_index = (self.next_index + 1) % len(self.arr)
if self.front_index == -1:
self.front_index = 0
def dequeue(self):
# check if queue is empty
if self.is_empty():
self.front_index = -1 # resetting pointers
self.next_index = 0
return None
# dequeue front element
value = self.arr[self.front_index]
self.front_index = (self.front_index + 1) % len(self.arr)
self.queue_size -= 1
return value
def size(self):
return self.queue_size
def is_empty(self):
return self.size() == 0
def front(self):
# check if queue is empty
if self.is_empty():
return None
return self.arr[self.front_index]
def _handle_queue_capacity_full(self):
old_arr = self.arr
self.arr = [0 for _ in range(2 * len(old_arr))]
index = 0
# copy all elements from front of queue (front-index) until end
for i in range(self.front_index, len(old_arr)):
self.arr[index] = old_arr[i]
index += 1
# case: when front-index is ahead of next index
for i in range(0, self.front_index):
self.arr[index] = old_arr[i]
index += 1
# reset pointers
self.front_index = 0
self.next_index = index
用栈来实现队列: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
def push(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def pop(self):
if self.size()==0:
return None
else:
return self.items.pop()
class Queue(object):
def __init__(self):
self.stack = Stack()
def size(self):
return self.stack.size()
def enqueue(self, value):
self.stack.push(value)
def dequeue(self):
tmp = Stack()
for i in range(self.stack.size()):
tmp.push(self.stack.pop())
value = tmp.pop()
for i in range(tmp.size()):
self.stack.push(tmp.pop())
return value1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18q = Queue()
q.enqueue(1)
q.enqueue(2)
q.enqueue(3)
# Test size
print ("Pass" if (q.size() == 3) else "Fail")
# Test dequeue
print ("Pass" if (q.dequeue() == 1) else "Fail")
# Test enqueue
q.enqueue(4)
print ("Pass" if (q.dequeue() == 2) else "Fail")
print ("Pass" if (q.dequeue() == 3) else "Fail")
print ("Pass" if (q.dequeue() == 4) else "Fail")
q.enqueue(5)
print ("Pass" if (q.size() == 1) else "Fail")
reverse_queue返回反转后的队列。
- 相关类的定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78class LinkedListNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.num_elements = 0
self.head = None
def push(self, data):
new_node = LinkedListNode(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
else:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
self.num_elements += 1
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None
temp = self.head.data
self.head = self.head.next
self.num_elements -= 1
return temp
def top(self):
if self.head is None:
return None
return self.head.data
def size(self):
return self.num_elements
def is_empty(self):
return self.num_elements == 0
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
self.num_elements = 0
def enqueue(self, data):
new_node = LinkedListNode(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
else:
self.tail.next = new_node
self.tail = new_node
self.num_elements += 1
def dequeue(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None
temp = self.head.data
self.head = self.head.next
self.num_elements -= 1
return temp
def front(self):
if self.head is None:
return None
return self.head.data
def size(self):
return self.num_elements
def is_empty(self):
return self.num_elements == 0 reverse_queue函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9def reverse_queue(queue):
if queue.size() <= 0:
return queue
stack = Stack()
for i in range(queue.size()):
stack.push(queue.dequeue())
for i in range(stack.size()):
queue.enqueue(stack.pop())
return queue- 测试用例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21def test_function(test_case):
queue = Queue()
for num in test_case:
queue.enqueue(num)
reverse_queue(queue)
index = len(test_case) - 1
while not queue.is_empty():
removed = queue.dequeue()
if removed != test_case[index]:
print("Fail")
return
else:
index -= 1
print("Pass")
test_case_1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
test_function(test_case_1)
test_case_2 = [1]
test_function(test_case_2)