栈
1 栈的含义
栈是一种类似摞起来的盘子的数据结构,性质是后进者先出(Last In First Out, LIFO),也就是你只能拿走最上面的盘子,一个一个,然后拿走下面的盘子。 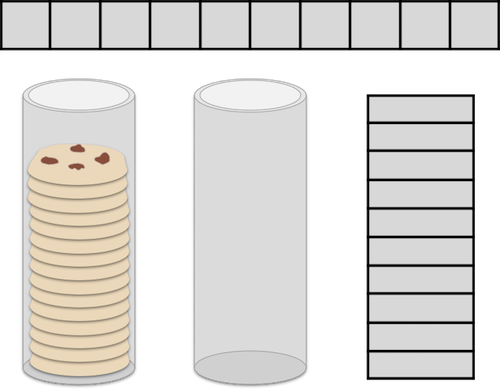
栈是一种方法或者说是思想,它可以用数组或者链表等等数据结构实现。
2 数组实现栈
基于python用数组实现一个Stack类,包含如下方法:
- push - 向栈顶增加一个元素
- pop - 删除栈顶元素并返回该值
- size - 返回栈的长度
- top - 返回栈顶元素的值
- is_empty - 判断栈是否为空,是则返回True,否则False
1. 创建并初始化Stack类
- Define a class named
Stackand add the__init__method - Initialize the
arrattribute with an array containing 10 elements, like this:[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] - Initialize the
next_indexattribute - Initialize the
num_elementsattribute
1 | class Stack(object): |
测试用例: 1
2
3foo = Stack()
print(foo.arr)
print("Pass" if foo.arr == [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] else "Fail")push 方法
- The method will need to have a parameter for the value that you want to push
- Remember that
next_indexwill have the index for where the value should be added - Once you've added the value, you'll want to increment both
next_indexandnum_elements
1 | class Stack(object): |
测试用例: 1
2
3
4foo = Stack()
foo.push("Test!")
print(foo.arr)
print("Pass" if foo.arr[0] == "Test!" else "Fail")
虽然python中的list是动态数组实现的,可以随意增加不用增加扩容处理,但是这里只是用list来代表一般的数组即定义时数组长度就固定了。 当栈的数组满的时候如果再增加元素就是Index out of range,所以需要进行扩容。
define the _handle_stack_capacity_full method:
- Define an
old_arrvariable and assign it the current (full) array - Create a new (larger) array and assign it to
arr. - Iterate over the values in the old array and copy them to the new array.
Then, in the push method:
Add a conditional to check if the array is full; if it is, call the
_handle_stack_capacity_full测试用例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23class Stack:
def __init__(self, initial_size = 10):
self.arr = [0 for _ in range(initial_size)]
self.next_index = 0
self.num_elements = 0
def push(self, data):
if self.next_index == len(self.arr):
print("Out of space! Increasing array capacity ...")
self._handle_stack_capacity_full()
self.arr[self.next_index] = data
self.next_index += 1
self.num_elements += 1
def _handle_stack_capacity_full(self):
odd_arr = self.arr
self.arr = [0 for i in range(2*self.num_elements)]
for i in range(self.num_elements):
self.arr[i] = odd_arr[i]
self.next_index = self.num_elements
self.num_elements += 14. 增加1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14foo = Stack()
foo.push(1)
foo.push(2)
foo.push(3)
foo.push(4)
foo.push(5)
foo.push(6)
foo.push(7)
foo.push(8)
foo.push(9)
foo.push(10) # The array is now at capacity!
foo.push(11) # This one should cause the array to increase in size
print(foo.arr) # Let's see what the array looks like now!
print("Pass" if len(foo.arr) == 20 else "Fail") # If we successfully doubled the array size, it should now be 20.size和is_empty方法Add a
sizemethod that returns the current size of the stackAdd an
is_emptymethod that returnsTrueif the stack is empty andFalseotherwise
1 | class Stack: |
测试用例: 1
2
3
4
5
6foo = Stack()
print(foo.size()) # Should return 0
print(foo.is_empty()) # Should return True
foo.push("Test") # Let's push an item onto the stack and check again
print(foo.size()) # Should return 1
print(foo.is_empty()) # Should return Falsepop方法
- Check if the stack is empty and, if it is, return
None - Decrement
next_indexandnum_elements - Return the item that is being "popped"
1 | class Stack: |
测试用例: 1
2
3
4foo = Stack()
foo.push("Test") # We first have to push an item so that we'll have something to pop
print(foo.pop()) # Should return the popped item, which is "Test"
print(foo.pop()) # Should return None, since there's nothing left in the stack
3 栈的应用
合法的出栈序列
问题描述:已知从1到n的数字序列,按顺序入栈,每个数字入栈后即可出栈,也可以在栈中停留,等待后面的数字入栈出栈后,该数字再出栈。求该数字序列的出栈序列是否合法。
思路:将1-n的数字序列一个一个入栈,每入一个就与“出栈序列”的队头进行比较,相同则出栈,不同则继续入栈。如果最后栈里面的元素无法弹空就说明不合法,否则合法。
括号匹配
在现实生活中经常用到栈来解决问题,例如数学公式中括号是否匹配的问题: \(((3^2 + 8)\*(5/2))/(2+6).\)
实现equation_checker函数,输入为字符串,如果括号都是匹配的返回True,否则返回False
1 | class Stack: |
测试用例: 1
2print ("Pass" if (equation_checker('((3^2 + 8)*(5/2))/(2+6)')) else "Fail")
print ("Pass" if not (equation_checker('((3^2 + 8)*(5/2))/(2+6))')) else "Fail")
最小括号反转
给定仅仅包含{和}的字符串,给出为了让括号匹配的最少的反转次数。
For
input_string = "}}}}, the number of reversals required is2.For
input_string = "}{}}, the number of reversals required is1.
If the brackets cannot be balanced, return -1 to indicate that it is not possible to balance them.
1 | def minimum_bracket_reversals(input_string): |
测试用例: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24def test_function(test_case):
input_string = test_case[0]
expected_output = test_case[1]
output = minimum_bracket_reversals(input_string)
if output == expected_output:
print("Pass")
else:
print("Fail")
test_case_1 = ["}}}}", 2]
test_function(test_case_1)
test_case_2 = ["}}{{", 2]
test_function(test_case_2)
test_case_3 = ["{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}", 13]
test_function(test_case_3)
test_case_4= ["}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{", 2]
test_function(test_case_4)
test_case_5 = ["}}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}{}", 1]
test_function(test_case_5)
后缀表达式
Reverse Polish Notation(逆波兰式)也叫后缀表达式,在后缀表达式中运算符( +, -, *, and /)出现在运算数的后面,即:3 1 + 4 *,也就是(3 + 1) * 4 (中缀表达式)。后缀表达式的优点就是对于计算机而言可以直接利用内存的栈式结构执行后进先出的顺序(遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中。)。
实现evaluate_post_fix函数,输入为后缀表达式(python的list),求出表达式的值并返回。
python中的
/进行浮点数的除法,结果为浮点数,利用int()将结果转为整数。
1 | ## 利用python的list模拟栈 |
测试用例: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16def test_function(test_case):
output = evaluate_post_fix(test_case[0])
print(output)
if output == test_case[1]:
print("Pass")
else:
print("Fail")
test_case_1 = [["3", "1", "+", "4", "*"], 16]
test_function(test_case_1)
test_case_2 = [["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"], 6]
test_function(test_case_2)
test_case_3 = [["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"], 22]
test_function(test_case_3)
4 LeetCode栈相关题目
LeetCode 225.用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通队列的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
- void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
- int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
- int top() 返回栈顶元素。
- boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例:
输入:
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
解释: 1
2
3
4
5
6MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
- 1 <= x <= 9
- 最多调用100 次 push、pop、top 和 empty
- 每次调用 pop 和 top 都保证栈不为空
我的解法:
1 | # |
——————
LeetCode 232.用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
- void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
- int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
- int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
- boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
- 你只能使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
我的解法:
1 | # |
—————
LeetCode 155. 最小栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
- push(x) —— 将元素 x 推入栈中。
- pop() —— 删除栈顶的元素。
- top() —— 获取栈顶元素。
- getMin() —— 检索栈中的最小元素。
示例:
输入:["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"] [[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]
输出:[null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
解释:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack(); minStack.push(-2); minStack.push(0); minStack.push(-3); minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3. minStack.pop(); minStack.top(); --> 返回 0. minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
提示:
pop、top 和 getMin 操作总是在 非空栈 上调用。
我的解法:
1 | # |
LeetCode 224.基本计算器
给你一个字符串表达式 s ,请你实现一个基本计算器来计算并返回它的值。
示例 1:
输入:s = "1 + 1"
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:s = " 2-1 + 2 "
输出:3
示例 3:
输入:s = "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)"
输出:23
提示:
- 1 <= s.length <= 3 * 105
- s 由数字、'+'、'-'、'('、')'、和 ' ' 组成
- s 表示一个有效的表达式
思路:
1 准备工作:
两个栈:数字栈和操作符栈。
栈中的操作:数字栈弹出两个数字,操作符栈出栈一个操作符,然后进行计算。
2 细节处理
左右括号:左括号出现时不能进行计算操作,直到右括号出现再进行计算。——>方法就是:可以使用一个变量compute_flag记录是否可以计算。
- 当遇到"+/-"时就可以计算,compute_flag = 1; - 当遇到'('时就不可以计算,compute_flag = 0;字符串处理:采用状态机的思路,具体处理可见代码。
解法:
1 | # |